Steel Hardness Converter: Rockwell C to Tensile Strength, HRC to BHN Calculator & Charts

You know the frustration of pausing a critical project to hunt down a reliable conversion chart. Manual lookups waste valuable engineering time and often lead to costly inaccuracies in material specification. That is why having a reliable steel hardness converter at your fingertips is essential for modern metallurgy. Whether you need a quick Rockwell C to tensile strength approximation or a robust HRC to BHN calculator for quality control, precision is non-negotiable.
At Nifty Alloys, we understand that certified data drives successful projects. This guide simplifies your workflow by consolidating essential formulas, charts, and tools into one resource. From using a steel hardness calculator to confirm heat treatment results, to applying a ksi to HRC conversion calculator for design verification, we cover it all.
By streamlining these conversions, you ensure your materials meet rigorous standards. Explore our Steel Hardness Converter Tool for instant, accurate calculations. For deeper insights into specific material behaviors, explore our comprehensive /alloy-steels-guide or review the specific /17-4ph-stainless-steel-properties for precipitation-hardening grades.

What is Steel Hardness and Why Convert It?
Understanding hardness scales is fundamental to selecting the right alloy for your application. In engineering terms, hardness measures a material's resistance to localized plastic deformation. However, different testing methods apply to different material grades and thicknesses.
- Rockwell C (HRC): This scale uses a 150kg load with a diamond cone indenter. It is the standard for harder steels, typically those used in tools and high-stress components.
- Brinell (BHN/HB): This method utilizes a 3000kg load with a 10mm carbide ball. It is ideal for castings and softer materials where a larger indentation averages out local inconsistencies.
- Vickers (HV): This test employs a diamond pyramid indenter. It provides a continuous scale applicable to a wide range of materials, from very soft to very hard.
Why do we convert between these scales?
- Speeding Material Selection: Quickly comparing a supplier's datasheet (often in BHN) with your design requirements (often in HRC).
- Preventing Heat-Treatment Errors: ensuring the steel hardness calculator output matches your post-temper quality checks.
- Linking to Tensile Strength: Estimating Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) from hardness helps verify if a part can withstand operational loads without destructive testing.
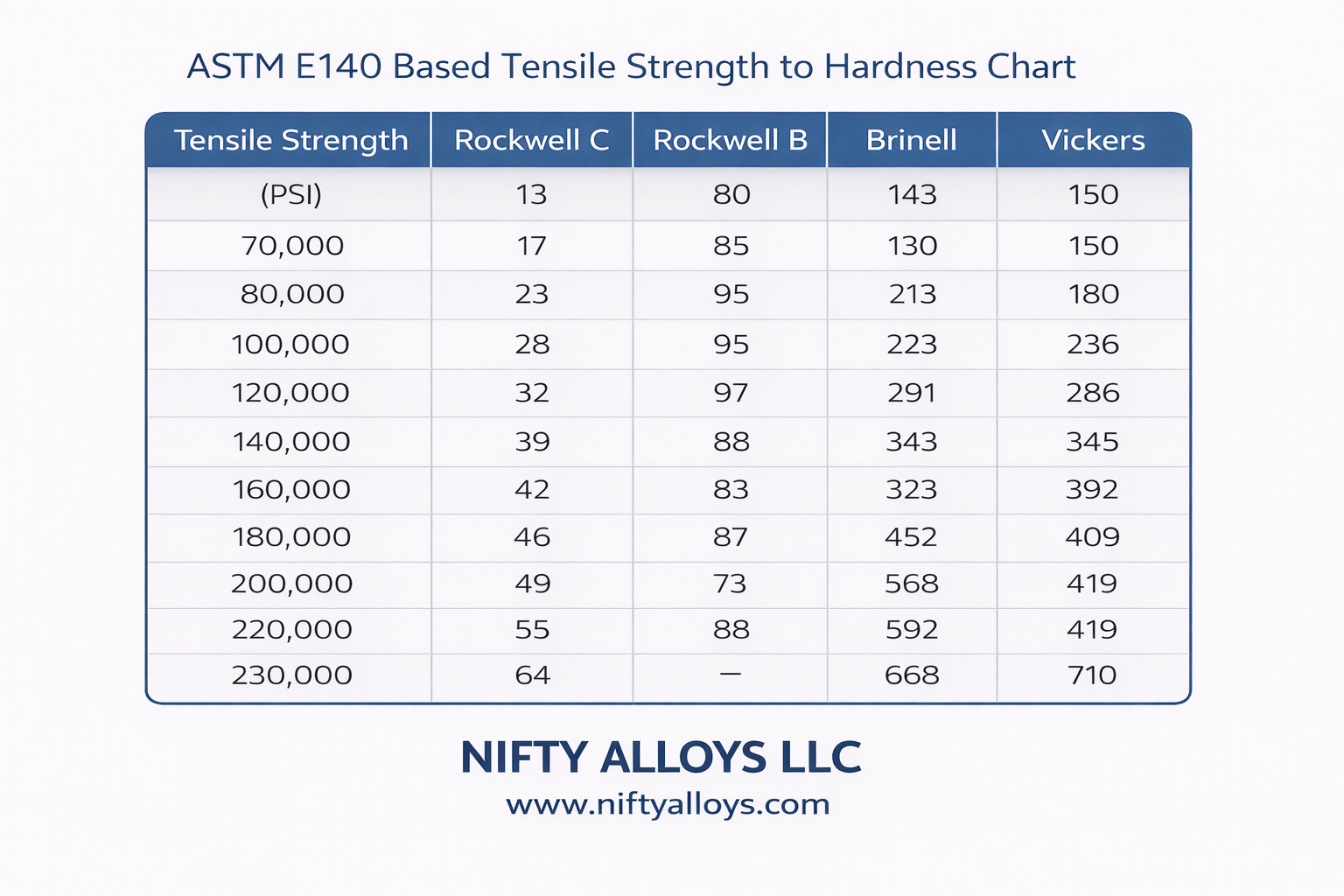
Steel Hardness Conversion Table: HRC to BHN, HV, Tensile
Below is a reference table based on ASTM E140 standards for non-austenitic steels. This table allows for quick cross-referencing between the most common industrial scales. Please note that while these values are standard for carbon and low-alloy steels, they are approximations.
Real-world deviations can occur due to composition and processing. Always verify critical components with certified Mill Test Reports (MTRs).
Below is a reference table based on ASTM E140 standards for non-austenitic steels. This table allows for quick cross-referencing between the most common industrial scales. Please note that while these values are standard for carbon and low-alloy steels, they are approximations.
Real-world deviations can occur due to composition and processing. Always verify critical components with certified Mill Test Reports (MTRs).
Rockwell C (HRC) | Brinell (HB/BHN) | Vickers (HV) | Tensile Strength (ksi) | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
| 68 | - | 940 | - | - |
| 65 | - | 834 | - | - |
| 60 | 620 | 697 | 285 | 1965 |
| 55 | 555 | 601 | 260 | 1793 |
| 50 | 477 | 513 | 225 | 1551 |
| 45 | 425 | 446 | 195 | 1344 |
| 40 | 375 | 392 | 170 | 1172 |
| 35 | 325 | 345 | 148 | 1020 |
| 30 | 285 | 302 | 130 | 896 |
| 25 | 250 | 266 | 115 | 793 |
| 20 | 234 | 240 | 100 | 690 |
Key Table Insights:
- High Hardness Range: Above HRC 60, Brinell readings become unreliable due to the deformation of the tungsten carbide ball.
- Tensile Correlation: Notice how HRC 20 correlates to roughly 100 ksi, while HRC 40 jumps to 170 ksi.
- Standard Compliance: These values align with ISO 18265 and ASTM E140, ensuring your data is audit-ready.
Rockwell C to Tensile Strength Converter
For engineers working without a chart, mathematical approximations provide a quick estimate. The relationship between Rockwell C hardness and tensile strength is linear for many carbon steels within a specific range.
You can use this formula for a quick Rockwell C to tensile strength calculation:
Tensile (ksi) ≈ 0.5 * HRC + 90
(Valid roughly for carbon steels with <0.5% Carbon)
Application Guidelines:
- Approximation Only: This formula is a rule of thumb. It works best for tempered martensitic structures.
- Error Margin: Expect a deviation of ±15%. Factors like grain size and alloying elements (Nickel, Chromium) influence the actual tensile strength.
- Verification: Never rely solely on this calculation for safety-critical applications. Always corroborate with a physical tensile test or MTR.
Using a verified hardness conversion calculator Excel sheet is often safer than manual calculation, as it can incorporate more complex regressions for higher accuracy.
KSI to HRC Conversion Calculator
Sometimes you have the tensile requirements and need to specify the hardness on a drawing. You can reverse the logic using this ksi to HRC conversion calculator formula:
HRC ≈ (UTS ksi - 90) / 0.5
Example Scenario:
- ** Requirement:** You need a material with a minimum tensile strength of 150 ksi.
- Calculation: (150 - 90) / 0.5 = 120 / 0.5 = 240? Wait, that is incorrect.
- Correction: Let's re-evaluate the linear relationship. If HRC 20 is ~100 ksi and HRC 40 is ~170 ksi.
-
- Slope ≈ (170-100)/(40-20) = 3.5.
- Revised linear approximation for the 20-40 HRC range: HRC ≈ (UTS ksi - 30) / 3.5.
- (150 - 30) / 3.5 ≈ 34 HRC.
Note: Always double-check derived formulas against the ASTM table provided above.
BHN to HRC, HV Calculators & Formulas
When you receive raw material, the certs often list Brinell (BHN) because it is the standard test for mill products. However, your finished part drawing likely specifies Rockwell C. A reliable HRC to BHN calculator is vital here.
BHN to HRC Formula:
For Brinell hardness numbers below 235, the relationship is roughly linear. However, for harder steels, the curve shifts. A common approximation used in many free online steel hardness conversion table tools is:
HRC = (BHN / 10.4) - 31
(Best used when BHN is between 250 and 400)
BHN to HV Formula:
Vickers and Brinell scales are numerically similar at lower hardness levels but diverge as hardness increases. A BHN to HV calculator often uses this relationship:
HV ≈ 1.05 * BHN + 0.45 * BHN^(1/2)
Excel Implementation:
To build your own hardness conversion calculator Excel tool, you can use logic functions to handle different hardness ranges.
- Excel Formula Example:
=IF(B2<235, (B2/10.4)-31, "Check ASTM Table") - Note: B2 represents your cell containing the BHN value.
These formulas help bridge the gap between incoming raw material checks and final quality control. Whether you need a Brinell to Rockwell converter or a Vickers to Brinell converter, these mathematical models save time during material receipt inspections.
Applications in Engineering Alloys
Why do we emphasize these conversions? Because in the field, mismatching hardness values can lead to catastrophic failure.
1. 17-4PH Stainless Steel:
This precipitation-hardening grade is ubiquitous in oil and gas.
- Condition H900: Typically yields HRC 40-47.
- Condition H1150: Typically yields HRC 28-37.
- Using an HRC to MPa calculator ensures that the condition selected meets the specific pressure rating of a valve body.
2. Weld Zone Analysis in Inconel:
When welding nickel alloys, the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) hardness changes.
- Converting micro-hardness readings (HV) to HRC helps field inspectors understand if the weld is too brittle.
- High hardness in the HAZ often correlates with susceptibility to Sulfide Stress Cracking (SSC).
3. Failure Analysis:
- If a shaft shears, measuring the hardness of the fracture surface can estimate the tensile strength at the time of failure.
- A tensile strength to hardness chart allows forensic engineers to determine if the material was heat-treated correctly originally.
4. Machining Setup:
- Knowing the HB to BHN calculator output helps machinists select the right insert grade.
- Material at 350 BHN requires different cutting speeds than material at 220 BHN.

Conclusion
Precision in material conversion is not just about numbers; it is about ensuring the safety and reliability of your engineering projects. For direct access to an advanced online conversion tool, visit our Steel Hardness Converter for instant calculations. By utilizing a robust steel hardness converter and understanding the relationships between Rockwell, Brinell, and Tensile strength, you eliminate guesswork.
We encourage you to integrate these formulas into your daily workflow. Remember, while calculations are helpful, Nifty Alloys always recommends verifying critical data with certified standards and mill test reports.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a steel hardness converter and how does it work?
A steel hardness converter estimates equivalent values between hardness scales (HRC, HB, HV) using empirical correlation tables, not direct formulas.
2. How do you convert Rockwell C (HRC) to tensile strength?
HRC is converted to tensile strength using ASTM E140 correlation charts, mainly for carbon and low-alloy steels as an approximation.
3. What is the most accurate HRC to BHN conversion method?
The most accurate method is using ASTM E140 or ISO 18265 tables, combined with knowledge of the steel grade and heat treatment.
4. Are hardness conversions based on ASTM E140 accurate for all steels?
No. ASTM E140 is not universal. Accuracy decreases for stainless steels, tool steels, nickel alloys, and non-ferrous metals.
5. How can I use a steel hardness calculator Excel sheet for quick conversions?
Enter the known hardness value, select the scale, and reference ASTM-based lookup tables embedded in the Excel sheet for fast estimates.
6. What’s the difference between Brinell (BHN), Vickers (HV), and Rockwell (HRC) hardness tests?
- BHN: Large ball indenter, bulk materials
- HV: Diamond pyramid, thin or precise samples
- HRC: Cone indenter, hardened steels
7. Can I convert hardness to tensile strength for stainless steel and tool steels?
Yes, but only as an approximation. Stainless and tool steels show greater variability due to alloying and heat treatment effects.
8. What is the formula to convert KSI to HRC?
There is no direct formula. Conversion from KSI to HRC relies on empirical charts, not mathematical equations.
9. Is there a reliable online hardness conversion calculator for engineers?
Yes. Engineering portals, ASTM-based calculators, and materials databases provide reliable conversion tools when used within their limits.
10. How do hardness values relate to heat treatment and material strength?
Heat treatment directly affects hardness. Higher hardness generally indicates higher strength, but reduced ductility.
11. Can I use these conversion tables for Inconel or titanium alloys?
No. ASTM E140 tables do not apply reliably to Inconel, titanium, or aluminum alloys. Use alloy-specific data instead.
12. What are the limitations of using ASTM-based hardness conversion charts?
Limitations include material dependency, heat treatment variation, surface condition effects, and non-applicability to exotic alloys.
13. Why do hardness-to-strength conversions vary across alloy types?
Different alloys have different microstructures, strengthening mechanisms, and responses to heat treatment, affecting correlations.
14. How can I check hardness conversion in Excel using BHN and HV values?
Use ASTM E140 reference tables, apply lookup functions, and clearly label results as estimated equivalents.
15. Which standard governs steel hardness conversion testing: ASTM E140 or ISO 18265?
Both are valid. ASTM E140 is widely used globally, while ISO 18265 is preferred in EN-based and European applications.

Looking for a reliable 17-4PH stainless steel supplier in Saudi Arabia? Nifty Alloys exports certifi...

For procurement managers and mechanical engineers, understanding these differences is essential. A m...

This guide provides an in-depth look at tool steel grades, their specific technical properties, and ...

This guide provides a technical deep dive into AISI 4140 mechanical properties across various condit...

Elevate Your Projects with
with
 Our Superior Steels
Our Superior Steels





